We have enhanced permission levels for Custom User Roles. This new functionality helps administrators to better control access levels that each of their Users and Groups have.
Available Custom Role Levels
We have added Module and Folder access permission configuration capabilities for Custom User Roles, to provide more granular governance options.
For default User role permissions:
- Admin and Author have View/Create/Edit/Delete access to all Folders. For any new Folders that get added, these Roles will automatically get View/Create/Edit/Delete permission as well.
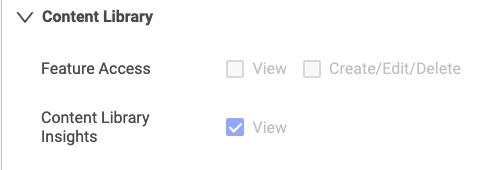
- The Reporter role has View permission for Content Library Insights (analytics) as shown below.
- The Revenue role has View and Create permission for Revenue Intelligence Module as shown below.

New permission levels now available for Custom Roles as follows:
- View Only or Create/Edit/Delete permissions can be set for entire Modules.
- View Only or Edit/Delete Experiences permissions can be set for any User by Business Unit/Folder.
- View Only options are configurable for those Experiences outside of a User’s Business Unit/Folder.
- Users can clone Experiences from Business Units/Folders where they have View permission.
Restricting Folder access can be configured for Custom Roles only, not for Default Roles (Admin, Author, Reporter, Revenue). However, you can clone one of the Default Roles and then modify its permissions to create a Custom Role.
As an Administrator, you can add governance to any User Role for any Module as you see fit. You can also group your Users by Business Unit and apply permission levels to a Business Unit. The screen capture below is a view of all of the Modules available on the Product Permissions tab.
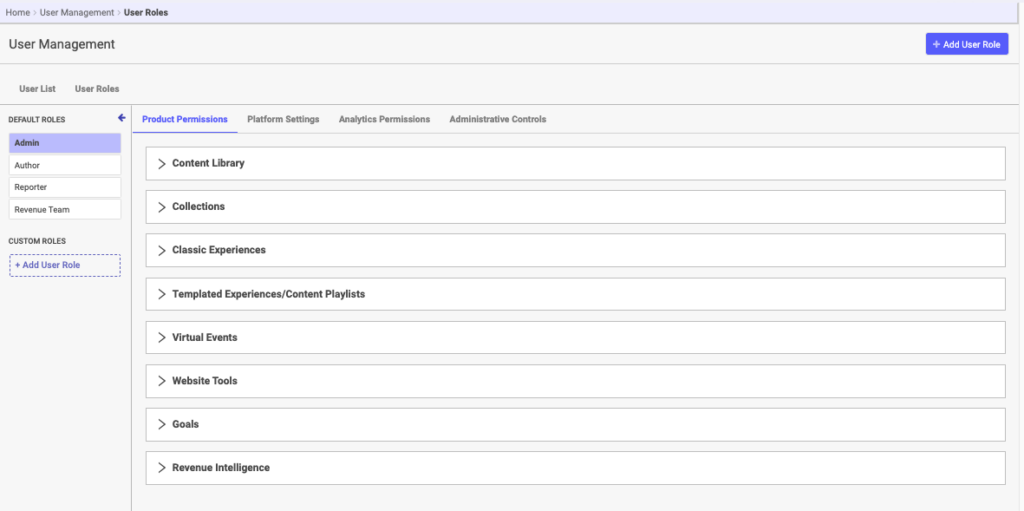
To see what permission options are available in each Module, click the arrow to expand its menu.
You may select each tab on the User Management page and grant or restrict permission levels on each one.
Note: If you are cloning a Default Role such as Admin or Author, you want to ensure the new Role does not have access to everything an Admin Role has, and so you will want to click through each of the tabs on this page.
- Product Permissions
- Platform Settings
- Analytics Permissions
- Administrative Controls
Below is an example of how a Module Access menu appears. To grant View or Create/Edit/Delete privileges for an entire Module, use the checkboxes at the top.
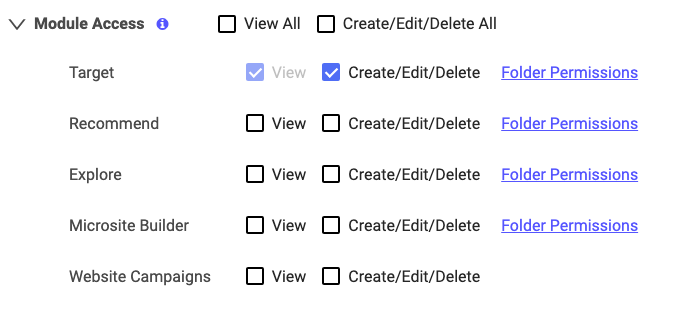
The Importance of Conferring View Permission Level
Administrators can give User Roles permission to View Folders that are managed by other Business Units besides their own. Giving your Users View permission for Modules and Folders outside of their own Business Unit enables Users to explore and clone Experiences (Standard and Templated) from other Business Units. This is helpful for sharing ideas (via Experiences) among Business Units.
By cloning an Experience, a User can edit and modify an Experience without affecting the original version.
How to Grant Create/Edit/Delete Permissions at the Module and Folder Level
There are two levels of permissions available for your Users – Modules and Folders. Creating these levels of permission can be tedious if you set up one User’s permission at a time. This is why Business Unit categories come in handy.
Here is an example of creating a Custom Role and adding Business Units to the Custom Role.
- Plan your Business Unit structure with all of the different groups and their desired permission levels needed for your organization. Learn about content tag configuration.
- Create a Custom Role that you want to include with one of your planned Business Units.
Note: It’s usually a good idea for the Role and the Business Unit to have the same name as each other to prevent confusion later.
- Edit the permission levels you want this Custom Role to have. Save your changes.
- Create or edit User Roles on the User List tab, and in each profile, assign them to the relevant Business Unit you have planned.
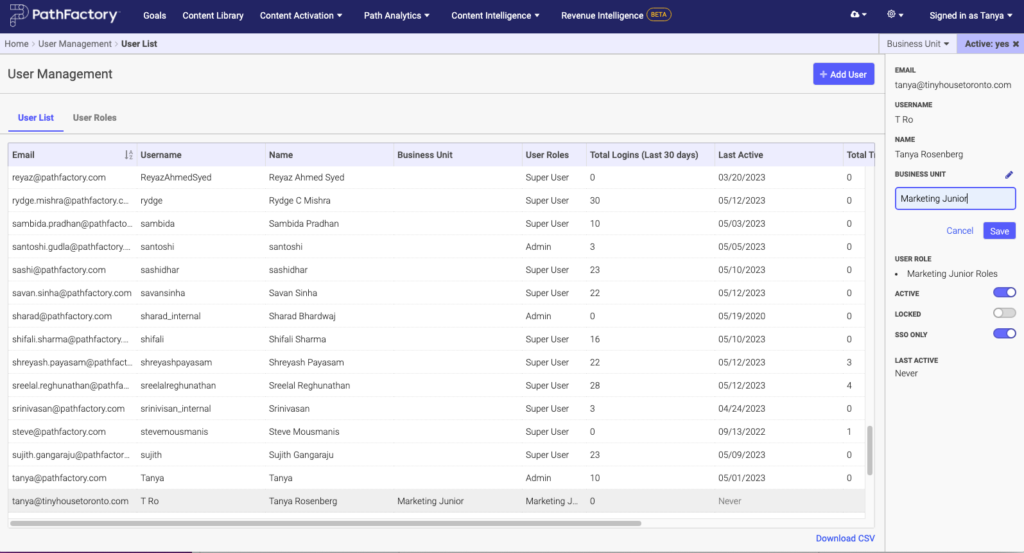
- Now your Users are grouped by Custom Role and Business Unit.
By using this method, you can edit permission for specific Business Units and grant permission for several Users at a time instead of for an individual User. For more detailed instructions on how to set up a Business Unit, please read the Release Notes I documentation.
Modules Permission
Module permission allows your User to View or Create/Edit/Delete within the entire Module, sub-Modules, Folders, and sub-Folders.
You can grant View or Create/Edit/Delete permission to control a User Role’s ability to create Folders and Experiences within a Module. For example, if a Custom Role is granted View access but not granted Create/Edit/Delete permission, they can View the Folder contents for a Module but cannot change the Folder’s contents.
The permissions set at the Module level are applied to its Folders as well by default. However, if you want different Folder-level access permissions, you can configure that access to be specific to the Folder level.
Folders Permission
Folder permission lets you restrict User permissions to View or Edit/Delete Folder contents within a Module. If Folder permissions are configured for a Custom Role, that permission overrides the permissions that had been set up for that Module. Cloning lets users with View permission can copy Experiences from Folders for which they have View permissions, and save the cloned Experiences into a Folder where they do have Edit/Delete permissions.
Example of Module and Folder Permission
For example, Custom Role X has View access to Folder A and Edit/Delete access to Folder B. Their View access allows them to see and clone Experiences from Folder A. But since they do not have Edit/Delete permissions for Folder A, they cannot save/add their cloned experience into Folder A. However, this Custom Role has been given Edit/Delete permission for Folder B, so they can save the clone to Folder B and edit it there.
See example of Clone icon in the screen capture (in the red rectangle) below.
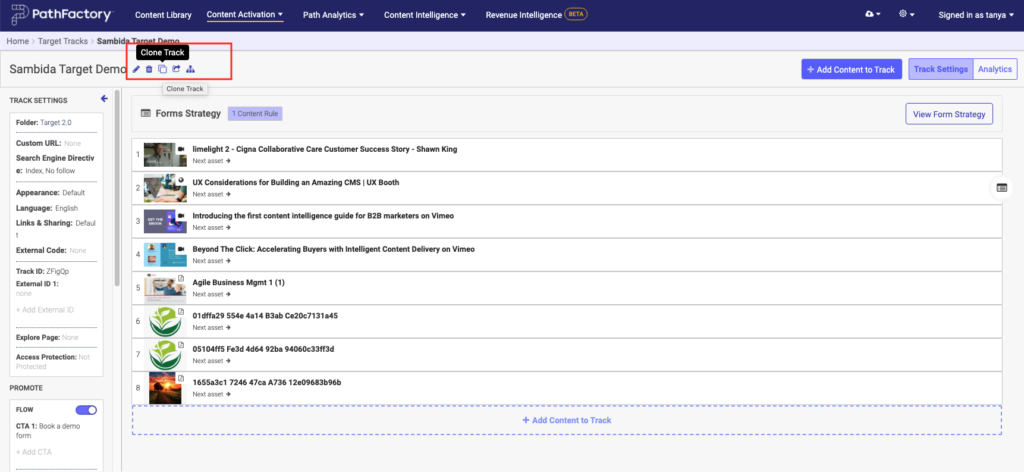
Example of Cloning an Experience
When you create an Experience, you can use the Clone From option, which lets you clone from an existing track. You can also open a track and click its associated clone icon. It will clone the track you are on and allow you to add a name and assign it to a Folder you select. See example in the screen capture below for creating a Standard Experience Target track.
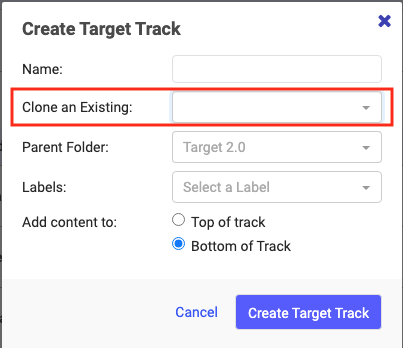
Again, the same rule applies where Users can clone the Experience and save it to a Parent Folder they have Edit permissions for.
How to Assign Module Level Permissions
With your new Custom Role selected, open the Module Access section to select the permissions you wish to confer onto the new User Role.
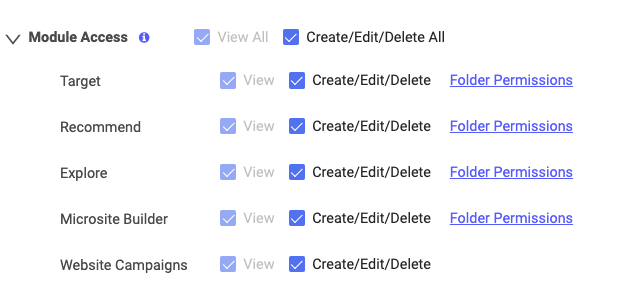
To give blanket permission to View All or Create/Edit/Delete All, activate the checkboxes listed at the top of the Module Access section.
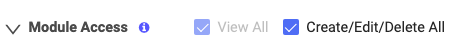
For each Module, you can give full View All or Create/Edit/Delete All permission for that Module by selecting its associated checkbox. To allow a user role to create content within a specific Module, you must select Create/Edit/Delete for that Module.
Folder Permissions is a link beside each Module that, if you wish, lets you select exactly which Folders your custom role is allowed to access within a Module. See the section below that describes Folder Level Permissions.
How to Assign Folder Level Permissions
The initial setup of the Folder level permissions are usually configured by an Administrator unless you have a Custom User Role where you have been granted User Management permissions.
- Permission level choices for Folders are View and Edit/Delete.
- If a permission is not configured at the Module level then it cannot be inherited by Folder-level permission.
- If you configure a permission level for a User in the Folder Permission settings, only the selected Folder(s) and associated permission will be updated. For example, if you grant Edit/Delete permission to a User for a parent Folder named ABC, the User is automatically granted Edit/Delete permission for the child Folder DEF. If you configure permission for just the child Folder DEF, the User doesn’t have Edit/Delete permission for Folder ABC.
- If Folder permissions are duplicated, they are automatically merged.
- For example, if in the first set of permission rules for a Custom User Role you grant View privilege to Folder A and then later you grant Edit/Delete privilege to Folder A, you will now have View and Create/Edit access to Folder A.
- You cannot hide the parent Folder as the child Folder inherits permission from the parent Folder. This means that, if a User Role doesn’t have access to a given parent Folder, then they will be able to click through to edit sub-Folders they have access to. But, for Folders that they aren’t permitted to View or Edit/Delete, the icons are greyed out. They will be able to select only the Folders for which they have View or Edit/Delete permission.
Example of Assigning Permission at Folder Level for a Sub-Module
For this example, you are assigning User Role permissions for the Target Module.
- On the Product Permissions tab, within the Module Access list, you have decided you don’t want a Custom User Role to be able to create Target tracks; you want that Custom User Role to have View permissions only. To achieve this, instead of clicking the checkbox beside Target in the Module menu, you select the Folder Permissions link. The following popup menu appears.
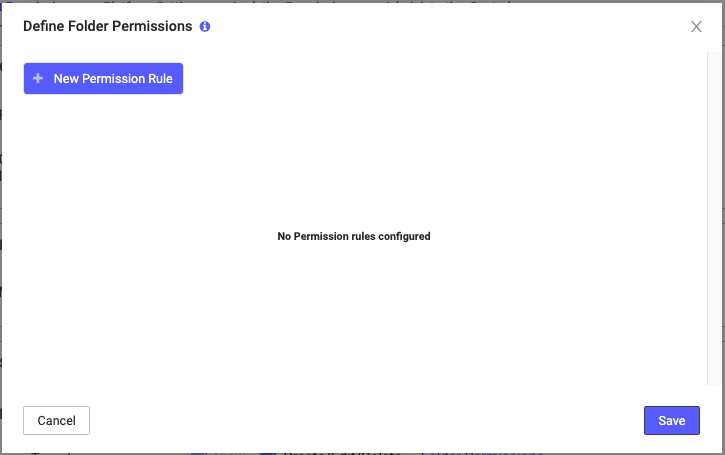
- This menu is empty because you haven’t assigned any permissions yet. To add permissions, click +New Permission Rule.
- A dropdown list of Folders appears, along with two checkboxes – View and Edit/Delete – and a Trash Bin icon.
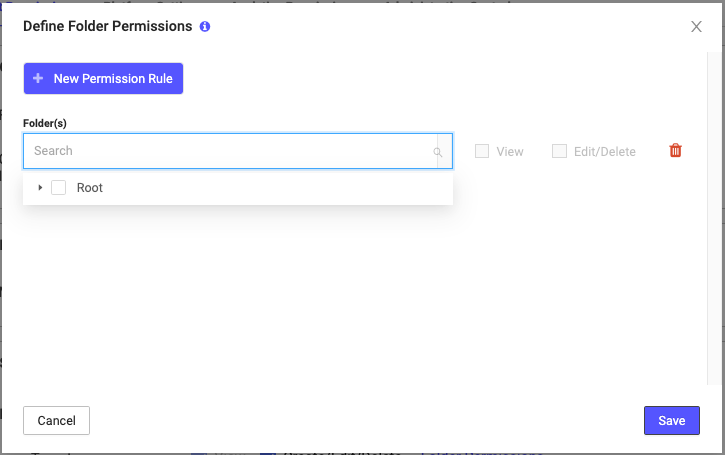
- When you click on the Folders list, you see Root available, because all the Folders for the Target Module are collapsed under this Folder. Select the small arrow beside Root to expand the Folders list.
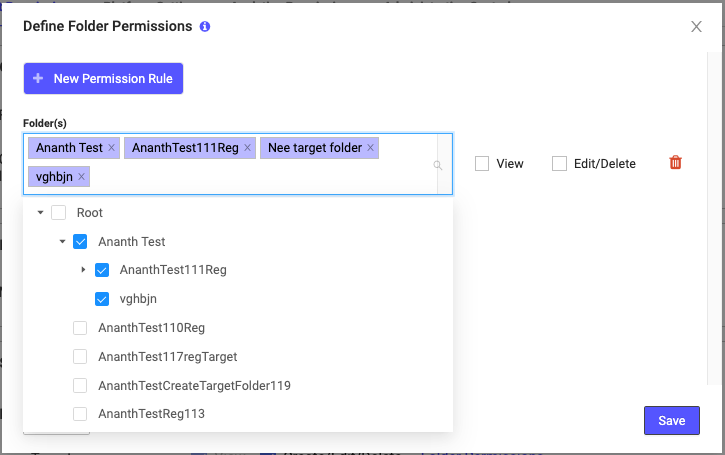
- You will notice that when you select a Folder, all of its child Folders are automatically selected. You can manually deselect whichever Folders or child folders you don’t want this Custom User Role to access.
- When you are finished selecting the Folders for this User Role, assign View as the permission level and click Save. You are returned to the Product Permission tab, in the Module Access list.
Repeat this process for each Module for which you want this user role to have View access.
How Custom User Role Permissions Work for Folder Hierarchies
If a user has permission to Edit/Delete a Folder and then creates a new child Folder within that Folder, they will have Edit/Delete access to the child Folders. Child Folders inherit the permission level of their parent Folder.
Example of Providing Access to Parent Folders and Their Child Folders
If Custom Role Y has access to all parent Folders (e.g. all HQ Folders), and you create a new Folder HQ1 under HQ, then Custom Role Y would automatically have access to that new Folder.
For example, if Custom Role A has View access to Folder 1 (e.g., “RC-NL” in the screenshot) and a User with Edit/Delete access creates a child Folder 1A (e.g., “Marketing” in the screenshot), then any Users assigned Custom Role A will have the same permissions for Folder 1 and Folder 1A by default.
If Custom Role X has access to only one child Folder under a parent Folder (e.g. RC-US under HQ), and if you (as Administrator) creates a new Folder RC-CA under HQ, then Custom Role X would not automatically have access to that new Folder. You would have to explicitly give permission to Custom Role X to access that parent Folder.
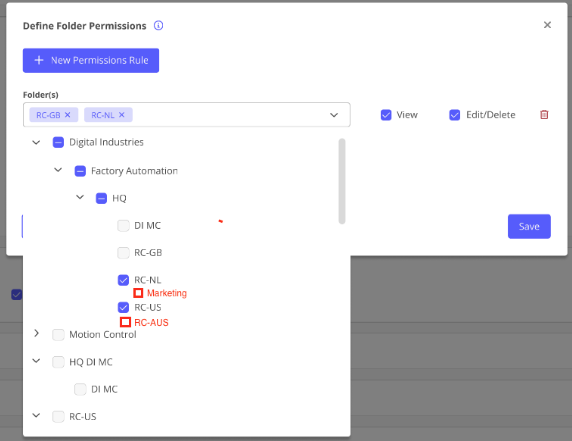
Custom Roles can clone Experiences to the Folders for which they have Edit/Delete permissions. They cannot add or save a cloned Experience to a Folder they have View only or no access to.
Once you have set up your Custom Role, you can assign this Custom Role to other users you want to have access to those Folders and Experiences.
How to Create a Custom User Role
To get started with any of these permissions, follow these steps.
- Click on your Login name and then select User Management.
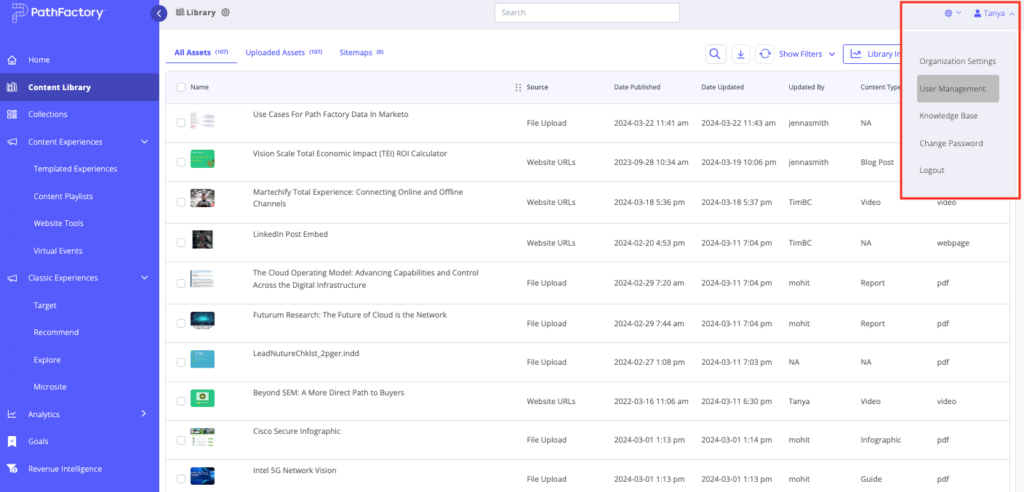
- Now select the User Roles tab.
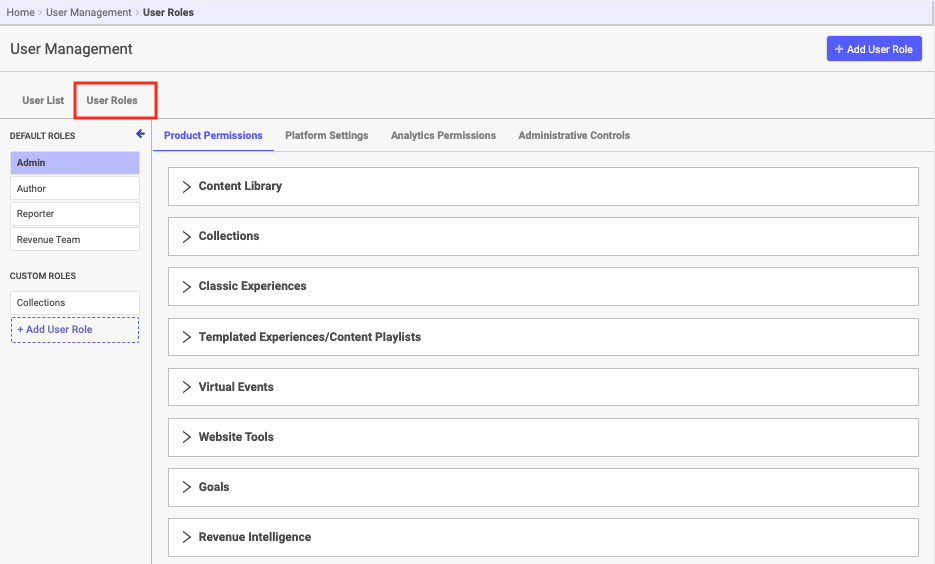
- On the top right of the screen, select +Add User Role. A popup menu appears.
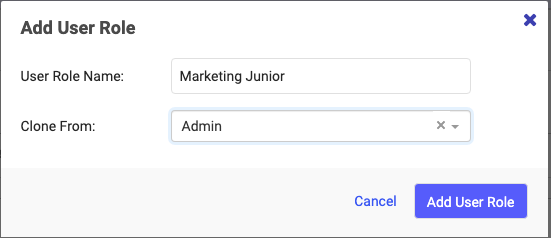
- You can create a new Role or clone any of the Default Roles and change/grant permissions as needed. (Cloning can save you time instead of starting from scratch.)
- Assign a name to the new Custom Role – e.g., “Custom Role – Marketing Intern” or “Custom Role – Consultant, Project ABC.” Then click Add User Role. You will now see your newly created Role in the list of all User Roles within the Custom Roles section (you may have to scroll down to the bottom of the User Roles to see it).
For more information about User Roles, read What are the Different User Roles?
Views: 87
